- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
- How to Design Isolated CAN Systems With Correct Bus Protection: link
There are some parameter that are necessary to be checked like Vabs: absolute maximum voltage rating at BUS terminals CANH, CANL and common mode Recommended common mode voltage at these terminals, while choosing the TVS diode clamping voltage Vclamp and Breakdown voltage Vbr.Let's take an example.
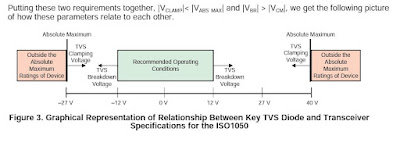
ISO1050 CAN transceiver device can withstand -27V to 40V at their CANH and CANL terminals and Recommended operating condition says -12V to 12V common mode voltage. In order to protect this device from -27V to 40V of ESD signals, TVS diodes are used at these terminals. While choosing TVS diode clamping voltage must be less than the absolute maximum voltage rating of the device and Breakdown voltage of TVS diode must be greater than the common mode Vcm voltage but less than the absolute max rating Vabs.
|Vclamp| < |Vabs| and |Vbr| > |Vcm|
Use this figure to make better decision while choosing the TVS diodes.
For ISO1050, CPDT-12V is a good choice as this ESD suppressor device or TVS diode has 25V of clamping voltage at peak pulse current Ipp of 1A and has Vbr of 13V. But ESDCAN05 has 61V of clamping voltage at Ipp of 3A and Vbr of 39V, so ESDCAN05 is a bad choice for ESD protection of ISO1050.
Another example.
SN65HVD230 CAN device has absolute maximum rating of -25V to 25V and Vcm is -2 to 7V. SZMMB5V6ALT1G is a bad choice because it has Vclamp of 8V at 3A of Ipp and Vbr of 5.6V.
For more info on CAN transient protection specially by using a choke follow this link.
More to come...
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Comments
Post a Comment