AFE: Audio Front End Pipeline
Typical AFE Features in DSP:
An AFE pipeline often includes components like:
-
AEC (Acoustic Echo Cancellation) → removes echoes from loudspeakers.
-
NS (Noise Suppression) → reduces background noise (fans, traffic, etc.).
-
AGC (Automatic Gain Control) → keeps voice levels consistent.
-
Beamforming → combines signals from multiple microphones to enhance the target direction.
-
VAD (Voice Activity Detection) → detects when speech is present vs. silence/noise.
-
Barge-in support → allows detecting user speech while system prompts are playing.
Why it matters:
-
Improves audio quality before sending it to ASR (automatic speech recognition) engines.
-
Optimizes resource use on embedded systems by running preprocessing close to the microphone.
-
Enhances robustness of voice-controlled devices in noisy or far-field conditions.
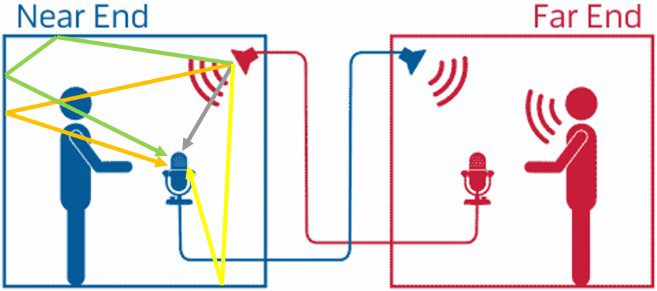
Audio Echo Cancellation (AEC)
Audio Echo Cancellation (AEC) is a signal processing technique designed to eliminate acoustic feedback caused by a system's own output being re-captured by its input—commonly occurring in full-duplex communication systems like speakerphones, conferencing systems, or voice assistants.
Problem Context
In a typical hands-free setup:
-
A far-end voice is played through a loudspeaker.
-
That audio is picked up again by the system’s microphone (along with the near-end speaker’s voice).
-
The far-end user hears their own voice echoed back, with a delay.
AEC aims to remove this echo path contribution from the microphone signal, enabling clear full-duplex communication.
ANC – Active Noise Cancellation (or Control)
Definition:
ANC is a real-time signal processing technique that uses destructive interference to cancel out ambient noise. It generates an anti-noise signal that is phase-inverted relative to the unwanted sound, thereby reducing the perceived noise at the ear or microphone.
Core Concepts:
-
Feedback ANC: Uses a microphone placed inside the headphone or near the ear to monitor the resulting sound. It's used to cancel low-frequency noise that leaks through passive isolation.
-
Feedforward ANC: Uses external microphones to capture ambient noise and generate anti-noise before it reaches the ear.
-
Hybrid ANC: Combines both feedforward and feedback microphones for better broadband cancellation.
ENC – Environmental Noise Cancellation
Definition:
ENC refers to microphone signal processing that removes environmental noise from voice capture signals, improving intelligibility of speech during communication (e.g., phone calls, voice assistants, or conferencing).
Core Concepts:
-
Utilizes multiple microphones to distinguish between speech (near-field) and noise (far-field).
-
Employs beamforming, spectral subtraction, Wiener filtering, or DNN-based noise suppression to isolate and enhance speech.
NOTE: Active Noise Cancellation (ANC) reduces unwanted ambient sounds in various environments, like offices, airplanes, and busy streets, to create a quieter experience for listening or focusing. Environmental Noise Cancellation (ENC) minimizes background noise during calls, making your voice clearer to the person on the other end.
Why All Three DSP Features Are Needed
| Feature | Role in TWS Earbuds | Why It’s Needed |
|---|---|---|
| ANC (Active Noise Cancellation) | Reduces unwanted environmental noise for the listener, improving audio immersion and speech intelligibility. | In noisy settings (train, plane, street), ANC suppresses low-frequency noise like engine hum, allowing the user to clearly hear music or voices. |
| ENC (Environmental Noise Cancellation) | Removes ambient noise from the user’s outgoing voice, so remote callers hear clean speech. | Without ENC, the far-end caller hears background chatter, traffic, wind, etc. ENC isolates the near-field (mouth) signal from far-field noise using multiple mics and beamforming. |
| AEC (Acoustic Echo Cancellation) | Removes playback audio (e.g., other caller’s voice) that leaks into the mic during calls. Prevents far-end echo. | When the user talks with someone over a call, the far-end speaker's voice is played through the earbud speakers. The mic can pick this up, causing echo unless cancelled. AEC ensures clean full-duplex conversations. |
Barge-In
In audio processing—especially in speech recognition and telephony systems—barge-in refers to the ability of a user to interrupt a system’s spoken prompt by speaking, and for the system to immediately stop playing audio and start listening.
For example:
-
In an IVR (Interactive Voice Response) system, the system might say “Please say or press 1 for sales, 2 for support…”.
-
If the user says “support” while the system is still speaking, barge-in allows the system to stop its prompt mid-sentence and immediately capture the user’s speech input.






Comments
Post a Comment